Excavation is key in construction and development. It lays the groundwork for successful projects. Knowing the excavation process is vital for contractors, project managers, and property owners.
PAR’s Services Ltd excels in excavation techniques. We offer expert solutions for projects across Canada. Our team ensures efficient and safe excavation, meeting industry standards.
The excavation process involves removing soil, rock, and materials. This prepares sites for construction. The techniques used depend on the project, site conditions, and engineering needs.
Key Takeaways
- Excavation is the critical first stage of construction projects
- Project timelines typically range from 3 days to 3 weeks
- Site assessment can impact 10-15% of total project budget
- Specialized equipment and techniques are key for success
- Safety and environmental considerations are essential
For top-notch excavation services, call PAR’s Services Ltd at +(604) 278-4445. Our experts are ready to help your project with the best excavation solutions.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Construction Site Excavation
Excavation is the first step in building a site. It turns raw land into a ready base for buildings. This process removes earth, rock, and materials to make room for foundations and structures.

Choosing the right excavation methods is key. Experts use different techniques to get the site ready and strong.
Definition of Excavation
Excavation means removing earth, rock, and debris to make space for buildings. Its main goals are:
- Preparing ground for building foundations
- Creating spaces for underground structures
- Installing utility lines and drainage systems
- Establishing proper site grading
Key Components of Excavation Projects
Excavation needs careful planning and action. Important parts include:
- Site Assessment: Checking soil conditions
- Equipment Selection: Picking the right machines for the terrain
- Safety Protocols: Putting in safety measures
- Geological Analysis: Knowing the ground’s makeup
Role in Construction Development
Excavation is the start of construction. It affects the project’s success a lot. About 40% of construction problems come from bad site prep.
Good excavation means a solid base for building. It stops problems later on and makes the site stable.
Effective excavation is not just about moving earth, but creating a precise, safe, and stable environment for construction.
What is Excavation Process

The excavation process is key for construction projects. It starts with preparing the ground and removing earth materials. Planning begins with a detailed site assessment and strategy to ensure success.
Vacuum excavation has changed how we dig. It can remove up to 2m³ of material per hour, beating manual methods. Modern excavation is precise, cutting down on errors and risks.
“Effective excavation is the cornerstone of successful construction projects” – Construction Engineering Quarterly
Here are the main steps in excavation:
- Site preparation and ground tracing
- Utility mapping and underground service detection
- Soil removal and material management
- Precise grading and leveling
- Dewatering and site stabilization
Professional contractors handle many tasks in excavation. They use bulldozers and vacuum excavators for safe and efficient work. Planning is key, considering soil, site conditions, and project needs.
Today’s excavation focuses on safety and efficiency. Vacuum excavation needs just one operator, lowering injury risks. This method also saves costs, making projects more affordable.
Types of Construction Site Excavation Methods
Excavation is key in construction. It involves removing earth, rock, and materials to get sites ready for building. The right techniques depend on the project, site, and geology.

There are many excavation methods, each tackling different construction challenges. Choosing the right one depends on the terrain, project size, and environmental factors.
Rock Excavation Techniques
Rock excavation is tough. Experts use special methods for rocky areas:
- Blasting for big rocks
- Hydraulic hammers for mechanical rock breaking
- Controlled fracturing
Small mini excavators are good for small rock jobs. Bigger ones handle bigger tasks.
Trench Excavation Procedures
Trench work is vital for utilities and foundations. It has specific features:
| Trench Type | Depth Classification | Common Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Shallow Trenches | Less than 19 feet | Utility lines, drainage systems |
| Deep Trenches | 19 feet or deeper | Complex infrastructure projects |
Basement and Foundation Excavation
Foundation work needs precision and special methods. Cut and fill excavation can move a lot of material daily. Basement work adds complexity, needing careful planning.
Choosing the right excavation methods is vital for success, safety, and efficiency. Knowing how to handle rock, trench, and foundation work is key to managing complex projects.
Essential Equipment and Machinery for Excavation

Construction excavation needs a wide range of specialized equipment. The right machines can greatly improve efficiency, safety, and project results.
Different projects need different equipment. Professionals use several key machines for complex earthmoving tasks:
- Excavators: Crucial for digging trenches and moving heavy materials
- Bulldozers: Powerful machines for breaking rock and reshaping terrain
- Backhoe loaders: Versatile for medium-sized urban construction jobs
- Crawler loaders: Combining excavator and backhoe capabilities
Modern excavation equipment has amazing tech advancements. Spider excavators can climb steep slopes, and zero swing excavators work well in tight spaces. These machines range from 13-ton to 80-ton, giving contractors great flexibility.
Rental options for excavation equipment have grown a lot. Contractors can now rent articulated dump trucks between 25-45 tons and wheel loaders with 1-7 cubic yard capacities. This variety means every project can find the right machinery.
Selecting the right excavation equipment is key to project success.
Safety is very important when using heavy excavation equipment. Regular maintenance, knowing what each machine can do, and proper training are vital. They help prevent accidents and ensure projects run smoothly.
Site Assessment and Pre-Excavation Planning
Starting a successful excavation project begins with a detailed site assessment. This step is key to ensuring safe and efficient soil excavation. Experts know that good planning before digging can lower risks and avoid project problems.
A good site assessment includes several important steps. These steps help avoid unexpected problems during digging. About 70% of construction delays come from poor site planning, showing how vital careful planning is.
Soil Testing and Analysis
Soil testing is a vital part of planning for excavation. It helps professionals understand the soil’s makeup and how it behaves. This knowledge lets them:
- Choose the right digging methods
- Spot any ground stability problems
- Find the best tools for the soil
- Anticipate environmental issues
Projects that do thorough soil testing see a 25% drop in soil problems. This shows how important this step is.
Topographic Surveys
Topographic surveys give valuable information about the site’s shape and height. They help engineers:
- Map the land’s shape
- Find out about drainage
- Plan the best digging strategies
- Look at possible environmental effects
Utility Location Services
Mapping utilities is a key safety step in excavation planning. Hitting hidden utility lines can cost $1,000 to $5,000 to fix. Professional utility mapping services prevent:
- Accidental service cuts
- Worker injuries
- Expensive damage to infrastructure
- Delays in the project timeline
With about 30% of digging projects hitting utilities, getting help with location is a smart move. It keeps the project safe and on track.
Required Permits and Legal Documentation

Excavation permits are key for any construction project. They ensure safety and compliance. Contractors need to know the rules to avoid legal issues.
The most common excavation permits include:
- Excavation or Grading Permit
- Utility Clearance Permit
- Environmental Permit
- Stormwater Management Permit
- Building Permit
- Erosion and Sediment Control Permit
Getting excavation permits is a detailed process. It can affect project timelines. Municipalities need lots of documents, like:
- Detailed project plans
- Site inspection reports
- Engineering calculations
- Environmental impact assessments
Not getting the right permits can lead to big fines. Fines can range from $50,000 for individual first offenses to $500,000 for corporate first-time violations. If you keep breaking the rules, fines can go up to $1,500,000.
Things to think about when applying for permits include:
- Plan early to avoid delays
- Have all your documents ready
- Know the local rules
- Include permit costs in your budget
The review process can take 10-30 days. This depends on how complex the project is. Using online forms and talking to local officials can help speed things up.
Site Preparation and Safety Measures
Excavation safety is key in any construction project. Good site prep and safety steps can lower risks and help projects finish well. Safe excavation starts with careful planning and managing risks well.

- Comprehensive site assessment
- Utility mapping and location services
- Soil analysis and stability evaluation
- Erosion control planning
Clearing and Grubbing Procedures
The first step is removing plants, trash, and topsoil. Excavation safety starts with a clean work area. Contractors must follow rules to clear the site well and protect the environment.
Safety Protocol Implementation
OSHA rules are key for excavation safety. Important safety steps include:
- Wearing personal protective gear
- Daily site checks by a trained person
- Using trench protection systems
- Good communication and emergency plans
| Safety Requirement | Specific Guidelines |
|---|---|
| Trench Depth Protection | Protective systems needed for trenches 5 feet deep or deeper |
| Equipment Safety | Stay away from underground services with mechanical gear |
| Worker Visibility | High-visibility vests needed in busy areas |
Emergency Response Planning
A good emergency plan is vital for safety. It includes clear escape paths, communication systems, and training for risks. Regular drills can make responses faster in emergencies.
Soil Management and Environmental Considerations

Soil excavation is a complex task that needs careful planning and management. It’s important to do environmental impact assessments to understand the effects on nature during construction.
Important things to consider in soil excavation include:
- Preventing soil erosion and sedimentation
- Minimizing dust and noise pollution
- Protecting surrounding ecosystems
- Managing waste generated during excavation
Research shows that bad soil management can harm the environment a lot. Sediment runoff can pollute up to 90% of nearby water bodies without control. Using erosion control can cut down sediment runoff by about 80%.
“Effective soil management is not just an environmental responsibility, but a critical component of sustainable construction practices.”
Dust suppression is key because excavation can increase dust levels by up to 50% nearby. Soil excavation teams need to use advanced methods to lessen these effects.
Waste management is also vital in soil excavation. About 30% of construction waste comes from excavation. Using strong recycling can boost material reuse to 60%, cutting down environmental harm.
Restoring the area after excavation is also key. Successful reclamation can bring back native plants and habitats. Studies show over 70% of areas can be restored to their natural state with the right approach.
Excavation Techniques and Best Practices
Excavation techniques are key to making construction sites safe and stable. Construction pros must think about many things when getting ready for site work and handling the ground.

Professional excavation needs exact methods for each project. Here are some top tips for preparing the ground well:
- Do a full site check before starting to dig
- Pick the right digging methods based on the soil
- Follow strict safety rules
- Use the right tools for the job
Proper Depth and Width Guidelines
Getting the right depth and width for digging is very important. Measurements must match engineering plans. Here are some main steps:
- Get the exact depth needed
- Make sure the width is consistent
- Think about any ground stability issues
- Keep safety in mind while digging
Slope and Grade Management
Good slope management stops ground collapse and keeps workers safe. Digging techniques must include smart grading to keep the ground stable and reduce risks.
Support System Installation
Support systems are vital for protecting workers and keeping the excavation stable. The right installation involves choosing the right shoring, bracing, and safety measures for each site.
Safety and precision are key to successful excavation projects.
Managing Ground Water and Drainage
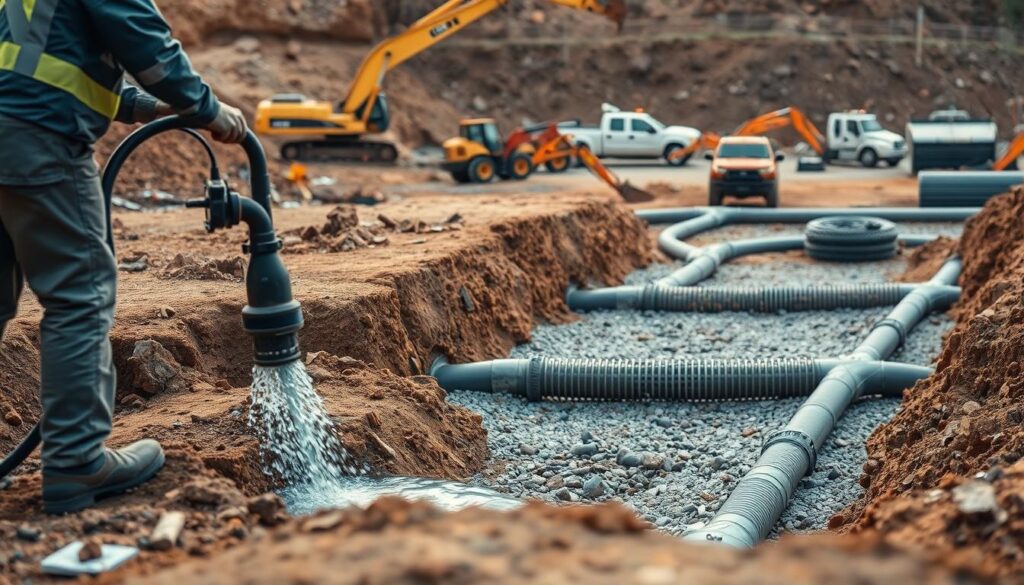

Managing groundwater is key to successful excavation. Construction teams need to control water levels and keep the site stable. Knowing how groundwater works helps avoid project failures and structural risks.
Effective strategies for managing groundwater include:
- Comprehensive site investigation
- Advanced dewatering methods
- Continuous water level monitoring
- Implementing protective barriers
Different dewatering methods work for different sites. The WellPoint method is good for sites up to 6 meters below the pump. Eductor wells can lower water tables from 10 to 45 meters. Gravity-based methods like open sump pumping are most economical in sandy or gravelly terrain.
Important things to consider in groundwater management are:
- Soil type and permeability assessment
- Hydraulic conductivity evaluation
- Groundwater flow direction analysis
- Environmental impact mitigation
Good drainage systems can cut project delays by up to 25% and reduce safety risks. Advanced geosynthetic technologies like geotextiles and geomembranes help control water seepage and improve structural integrity during excavation projects.
Proper groundwater management is not just a technical requirement, but a fundamental safety and sustainability practice in modern construction.
Quality Control in Excavation Projects
Quality control is key to successful excavation planning. It ensures precision and safety in construction projects. This is done through monitoring, documentation, and checking if things are done right.

Good quality control can cut down errors by up to 35%. This means excavation work will meet all the needed standards. Here are the main things for top-notch excavation projects:
- Systematic inspection procedures
- Detailed documentation requirements
- Comprehensive compliance verification
Inspection Procedures
Good excavation planning needs careful inspection. Inspections should be done by experts or independent groups to avoid bias. Skilled operators can cut excavation time by about 20% by checking the site as they work.
Documentation Requirements
Keeping detailed records is key to tracking project progress and quality. Excavation projects should have:
- Daily work logs
- Progress reports
- Photographic evidence
- Material testing records
Compliance Verification
Following the rules can lower legal issues by up to 50%. Using GPS-guided equipment can boost excavation accuracy by over 90%. This helps ensure everything is done right.
| Quality Control Metric | Improvement Percentage |
|---|---|
| Excavation Accuracy | 90% |
| Error Reduction | 35% |
| Legal Risk Mitigation | 50% |
With strong quality control, construction teams can greatly improve project results, safety, and efficiency in excavation planning.
Timeline and Project Management

Excavation planning needs careful timeline management for success. The project’s length changes a lot. This depends on how complex it is, the site conditions, and its size. Knowing these helps teams plan better and set realistic goals.
The time needed for excavation varies a lot. It depends on the project’s details:
- Small-scale projects: 2-7 days
- Medium-scale projects: 1-3 weeks
- Large-scale projects: Several weeks to months
Things that affect costs and time include:
- Soil conditions and terrain complexity
- Weather constraints
- Equipment availability
- Permit acquisition timeframes
- Contractor expertise
To plan well, teams need to be proactive. Early contractor engagement and detailed geotechnical assessments are key. They help understand how long the project will take and what challenges might come up.
| Project Scale | Typical Duration | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Residential Landscaping | 2-7 days | Limited area, minimal equipment |
| Commercial Building Foundation | 2-4 weeks | Complex site preparation |
| Infrastructure Project | 6-12 weeks | Multiple phases, extensive coordination |
Project managers know that being flexible is key. Unexpected problems like rocky ground or bad weather can make things take longer. Having extra time and keeping everyone informed helps deal with these issues.
Cost Factors and Budgeting Considerations
Excavation costs can change a lot, depending on the project type. Many things affect the budget. Knowing these factors is key for planning money in construction projects.
The size of the project matters a lot. From fixing a home’s foundation to big commercial jobs, the cost varies.
Equipment and workers are big parts of the cost. Contractors need to think about renting machines, paying workers, and dealing with site problems. The type of soil also affects the cost. Hard or rocky soil needs more time and special tools than soft soil.
PAR’s Services Ltd helps manage costs for excavation projects. They do detailed cost checks, site checks, and pick the right tools and workers. By looking closely at the project and soil, and using smart ways to estimate costs, they can save money.
Project managers should use smart budgeting methods. This includes using parametric estimation and quantity takeoff. These help predict costs, considering things like how easy it is to get to the site, seasonal issues, and surprises. A good financial plan helps avoid going over budget and makes sure the project is a success.
